Contract Architecture
Architecture
- Bungee's smart contracts serve as aggregators for DEXs, DEX aggregators, and bridges. A fundamental principle of Bungee’s smart contract architecture is the prioritization of modularity over upgradability. After deployment, a module becomes immutable, with the sole exception that it can be paused by the owner in the event of bugs.
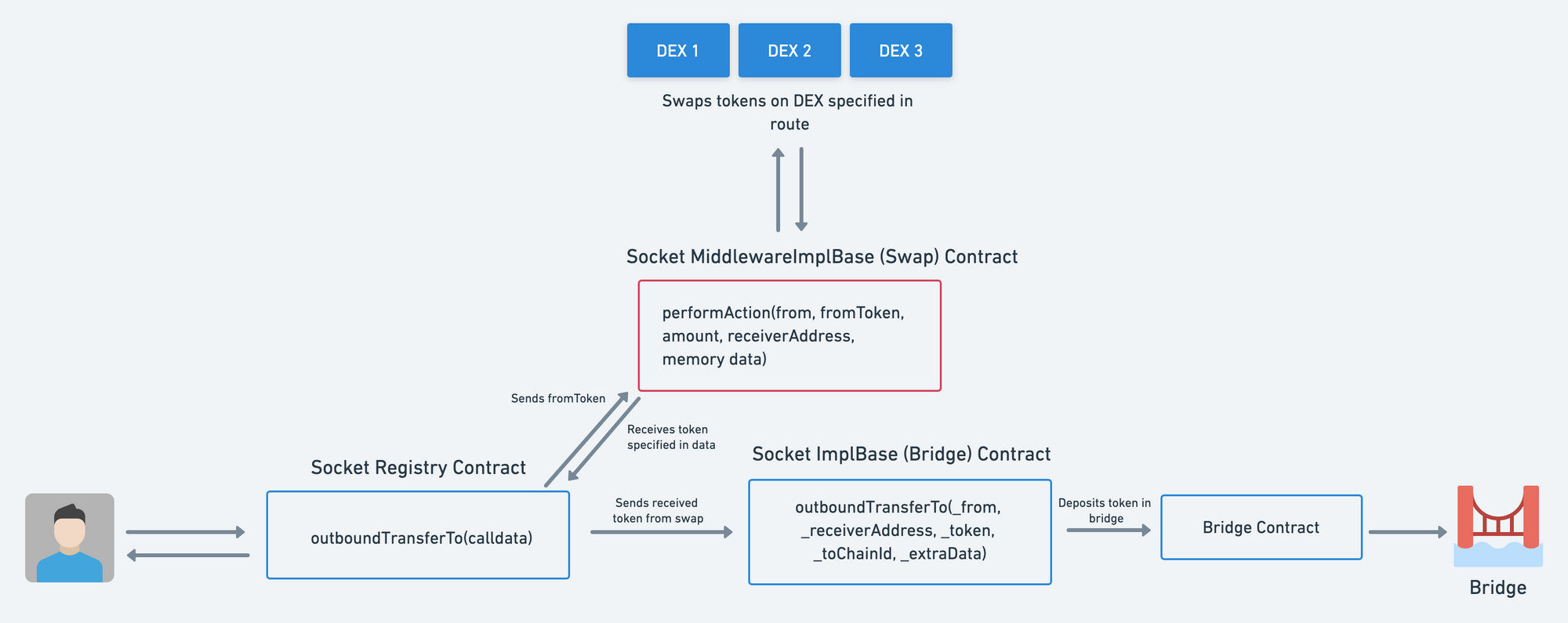
- To initiate a bridging transaction, users engage with Bungee's
Registry.solcontract. - Each DEX & Bridge has different functions and interfaces to initiate transactions. The Implementation contracts act as a middleware to interact with the DEX/Bridge contract functions. Once a route is added to the registry, the route data is immutable and it points to addresses of respective DEX and Bridge Implementations.
No proxies, immutable modules, Bungee's modularity pattern doesn't add any additional trust assumptions
User Interaction
- When a user initiates a transaction, tokens are sent to the Registry along with the callData for the bridging route. This data can be generated from the
/build-txendpoint or independently from the API. - The Registry decodes the
userRequestcallData and checks if aMiddlewareRequesthas been added in the callData. If there’s none, this implies the route doesn’t involve a swap and it can proceed directly to bridging. - If a
MiddlewareRequestis specified, the Registry will identify the DEX’sidand make a call to its implementation contract and initiate a swap. The swapped tokens are returned to the Registry. - Then, the Registry checks the
idof theBridgeRequestto identify which bridge the route specifies. - It then calls the Bridge implementation contract and initiates a bridging transaction with relevant function arguments decoded from the initial callData sent by the user. This initiates the bridging process and the user is expected to receive funds on the destination chain.